- WeAreHuman
- Posts
- Udemy | Gen Z in the Workplace: Welcoming the Next Generation (2024)
Udemy | Gen Z in the Workplace: Welcoming the Next Generation (2024)
This report explores the characteristics, values, and expectations of Generation Z in the workplace, emphasising their readiness for work and perspectives on learning, particularly with the integration of generative AI. Understanding Gen Z's needs is crucial for businesses attracting and retaining this demographic.

PEOPLE EXPECTATIONS
Udemy | Gen Z in the Workplace: Welcoming the Next Generation | This report explores the characteristics, values, and expectations of Generation Z in the workplace, emphasising their readiness for work and perspectives on learning, particularly with the integration of generative AI. Understanding Gen Z's needs is crucial for businesses attracting and retaining this demographic.
DID YOU KNOW?
“Did you know that Generation Z, born between 1997 and 2012, will account for 27% of the global workforce by 2025, making them the largest generation in the workforce by 2035?”
DID YOU SEE?
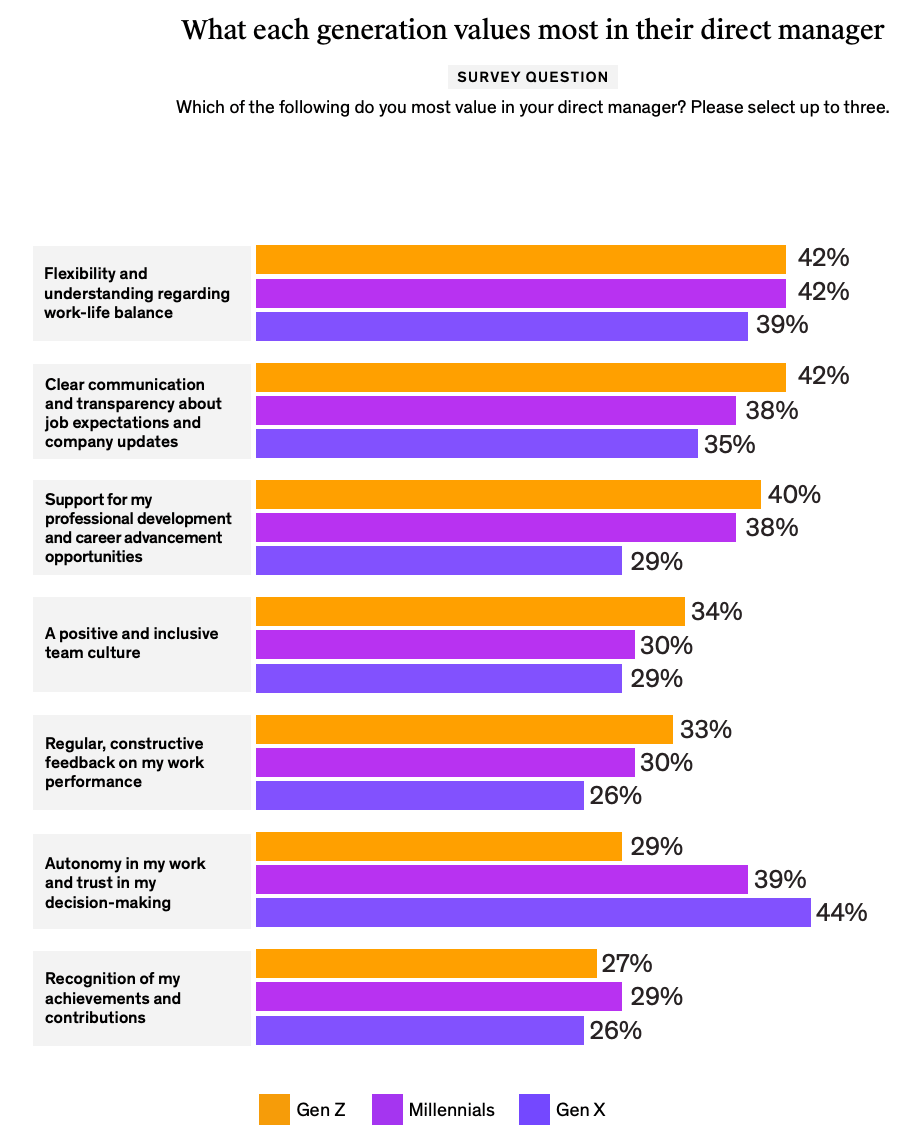
Figure: What Each Generation Values Most in Their Direct Manager
NEED AN EXECUTIVE SUMMARY?
Introduction
Generation Z, born between 1997 and 2012, is set to represent 27% of the global workforce by 2025. This generation is notably diverse, tech-savvy, and globally aware. Recognising what Gen Z seeks from work is essential for sustaining organisational growth as they become a significant part of the workforce.
Key Insights
Workplace Values: Gen Z prioritises flexibility and work-life balance (42%) and values clear communication and transparency from managers (42%). They also seek support for professional development (40%).
Sense of Purpose: A staggering 86% of Gen Z employees believe that having a sense of purpose is crucial for job satisfaction. Nearly 44% have declined job offers based on personal ethics or beliefs.
Learning Preferences: Gen Z prefers guidance from senior leadership and learning teams rather than peers, indicating a solid engagement with organisational learning initiatives.
Work Preparedness: While 93% of Gen Z feel at least somewhat prepared for workforce demands, only 35% feel very prepared. This reflects their awareness of the skills needed for success.
Essential Skills: The top skills Gen Z believes are necessary for future careers include programming (36%), artificial intelligence (30%), communication (30%), critical thinking/problem-solving (26%), and creativity/innovation (22%).
Recommendations
Create Learning Opportunities: To foster engagement and develop meaningful learning and upskilling programs that align with Gen Z’s values and career aspirations.
Promote Flexibility: Implement policies that support work-life balance to attract and retain Gen Z talent.
Encourage Open Communication: Ensure clear communication and transparency are prioritised at all management levels.
Invest in Professional Development: Offer robust professional development opportunities that resonate with Gen Z's desire for career advancement.
Utilize Generative AI in Learning: Integrate generative AI technologies into learning experiences to enhance engagement and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Understanding Generation Z's unique perspectives on work is vital for organisations aiming to thrive in a rapidly changing landscape. Businesses can effectively engage this emerging workforce by aligning workplace practices with their values, fostering a culture of continuous learning, and addressing their specific needs. As Gen Z continues to grow in numbers within the workplace, their influence will shape organisational strategies.